NiCad Battery Charger
The charging current required for each battery is usually different. A general rule-of-thumb is to use a current equivalent to 10 % of the battery capacity. However, you should always consult the datasheet for your battery to determine the precise charging current required. For rechargeable NiCad batteries with capacities of 600 mAh, 700 mAh, and 800 mAh, the charge current is 60 mA, 70 mA, 80 mA, respectively.
Cowboy Methods
I have seen cowboys simply connect a battery to a voltage source and expect it to be charged, however a voltage source will not charge the battery properly. A rechargeable battery requires a constant current source in order to be charged.
You need to provide the precise current level to charge the battery, and many datasheets often contain this information for the battery in question.
Voltage Source to a Constant Current Source
Producing a constant current source from a voltage source is very simple, and almost any three-pin positive voltage regulator IC works for this purpose. Most people will have the commonly available 7805 voltage regulator, hence that is often the component used by hobbyists.
The 7805 pinout is such that the leftmost pin is input, centre pin is the ground, and the rightmost pin is the output. Please refer to the 5 V Voltage Regulator article if you need more information.
Battery Charger Circuit
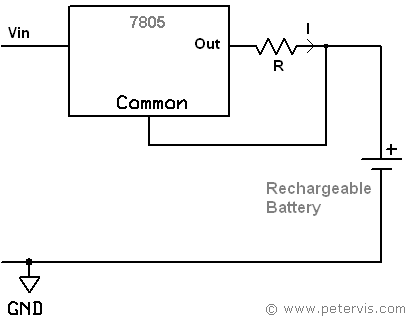
In the circuit diagram above, you can see that the circuit is different from the usual voltage regulator configuration. A resistor R between the centre pin and the output pin will have a constant voltage of 5 V across it. How do I know that it will be 5 V? Because this is a 5 V regulator! However, more importantly, the current, through resistor R is dependent upon Ohm's Law, and this current is also a constant.
If we were to be charging an 800 mAh NiCad battery, then the charge current would be given by C / 10, where C is the charge capacity of the battery in mAh. In this case it would be 80 mA or 0.08 A.
Using Ohm's Law, R = V / I, we can calculate the value of the current limiting resistor.
R = (5 / 0.08) = 62.5 Ω
You then look at the standard resistor values chart to find the nearest highest value, which in this case is 68 Ω
Although we now have a resistor value, we must also find its power rating. For this we use the formula Power = current (I) × voltage (V)
In this case, Power = (0.08 × 5) = 0.4 W
Hence a 0.5 W or 0.6 W resistor ought to work, however 1 W is even better as it provides better dissipation and a margin of safety.
Resistor (R) Values
| Battery Capacity C (mAh) | R (Ω) |
| 2000 | 27 |
| 1000 | 56 |
| 800 | 62.5 |
These are the current limiting resistor values if you were using a 7805 voltage regulator.
Note that although the 7805 voltage regulator is capable of providing a maximum of 1000 mA (1 A) current, it is best not to draw any more than 600 mA.