Transistor Symbol
The bipolar transistor symbol is one of the most difficult to draw, because there are NPN and PNP versions as well as the direction of their arrows to consider. The teacher usually never explains how to draw them; therefore, this page might help those who want to know how to draw qualified symbols.
There are many transistor symbols on the top ranks of Google drawn by "experts", however, nearly all of them are wrong. Here are some proper symbols that you can study. These are according to the ANSI / IEEE specifications. The proportions will fit a 1 × 1 grid, so it is better to practice drawing these on grid paper first. I have left some dots as a guide.
Transistors are "bipolar" because holes and electrons are both involved in carrying the charge. The electrons carry the negative charge to the positive pole, and the holes carry the positive charge to the negative pole. This is what the direction of the arrow indicates.
NPN Transistor
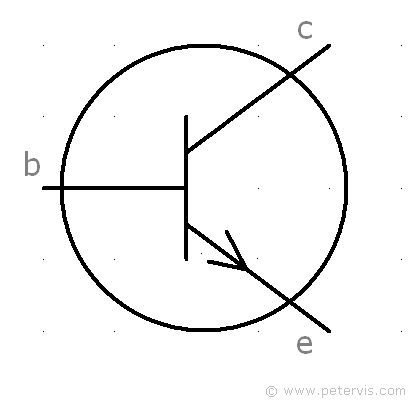
For a NPN transistor, the "arrow direction" is outward.
PNP Transistor
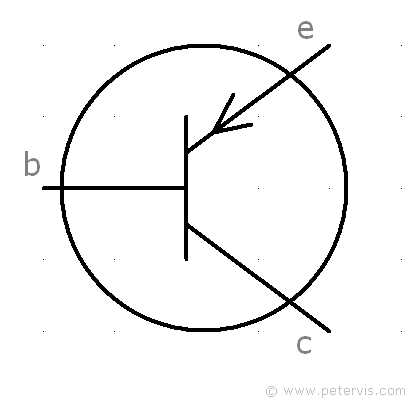
For a PNP transistor, the "arrow direction" is inward.
Gain Symbol
Transistors have two different types of gain symbols. One symbol indicates the dc gain, whilst the other indicates the ac gain, also known as small signal gain.
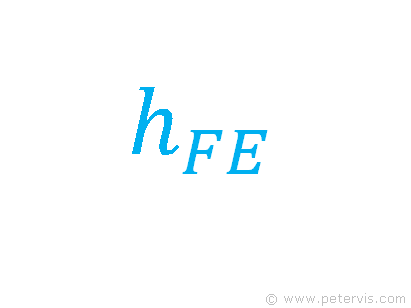
DC Current Gain
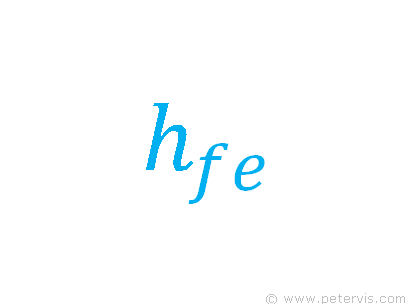
Small Signal Gain
Pinout
The pinout on the physical package does not always follow the electronic symbol. You therefore need the documentation of the transistor to figure out how the pins are organised.
For example, the BC546, BC547, BC548, and BC549 transistors come in a TO-92 package. When the flat side is facing you, the pins are collector, base, and emitter.